
Imagine you want to grow your money, but the stock market feels unpredictable, and traditional investments take forever to show returns. What if there was a way to control your risks while grabbing opportunities for higher rewards? Well, that’s exactly where options trading comes in.
Options trading isn’t just for experts or big investors; it’s a tool that allows anyone to hedge risks, speculate smartly, or even generate steady income. This guide will explain everything you need about options trading in India.
Options trading is a financial contract that gives you the right (but not the obligation) to buy or sell an asset at a specific price before a set date. This flexibility makes options trading a popular tool for investors looking to manage risks, speculate on market movements, or lock in profits without owning the underlying asset outright.
Unlike buying stocks directly, where you own a piece of the company, trading options involve predicting how the price of an underlying asset—like a stock, index, or commodity—will move within a specific timeframe. For instance, instead of purchasing shares of Reliance Industries, you can trade options on its stock to profit from price changes without tying up significant capital.
For example, instead of investing ₹1,00,000 to buy a stock, you might spend only ₹5,000 to trade an option on the same stock. This lower cost and the ability to hedge against market risks make it a favourite among both beginners and seasoned traders in India.
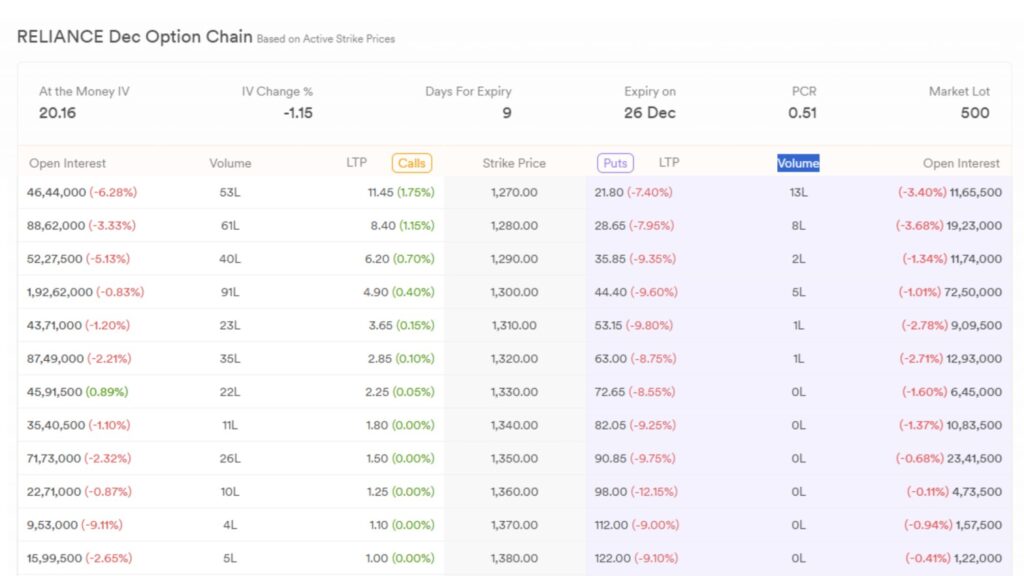
Here’s how an option might look for Reliance Industries (RIL) stock:
Options contracts are categorised into two main types: Call Options and Put Options. Each serves a distinct purpose, allowing traders to speculate on price movements or hedge against potential risks.
A call option gives you the right (but not the obligation) to buy an asset at a specific price (strike price) before a fixed date (expiration). You’d typically buy a call if you expect the asset's price to rise in the future.
Example:
Let’s say Reliance Industries (RIL) stock is currently trading at ₹2400.
How to Spot a Call Option:
When looking at an options contract, it might appear as follows:
RELIANCE 26 Dec 2500 CE
If the stock price goes above ₹2500, the call option becomes profitable, and you can either sell the option for a higher premium or exercise it.
A put option gives you the right (but not the obligation) to sell an asset at a specific strike price before a fixed expiration date. You’d buy a put option if you expect the underlying asset's price to fall.
Example:
Suppose Reliance Industries (RIL) stock is currently trading at ₹2400.
How to Spot a Put Option:
When looking at a put option contract, it might appear as:
RELIANCE 26 Dec 2300 PE
The put option becomes profitable if the stock price goes below ₹2300.
Yes, options are a type of derivative instrument. A derivative is a financial contract whose value is based on the performance of an underlying asset, such as stocks, indices, commodities, or currencies. In the case of options, the value of the contract is derived from the underlying asset's price movements.
Options trading has gained immense popularity among Indian investors due to its unique advantages over traditional stock trading. Here are some of the key reasons why traders prefer options:
Options trading offers various strategies to suit market scenarios, risk appetites, and trading objectives. Some of the most commonly used strategies are explained simply with practical examples tailored to Indian traders.
A long call involves buying a call option to profit from an expected rise in the underlying asset's price. This strategy is ideal if you believe the asset's price will rise significantly before expiry. It allows traders to leverage small capital for higher potential returns.
Example:
Suppose Infosys stock is trading at ₹1,400.
If the price doesn’t rise above ₹1,500, the option expires worthless, and you only lose the premium paid (₹20 per share).
A long put involves purchasing a put option to profit from an anticipated drop in the underlying asset's price. This strategy works well when you expect the stock price to fall significantly.
Example:
Hindustan Unilever (HUL) is trading at ₹2,600.
If the stock price doesn’t fall below ₹2,500, you lose only the premium paid.
A covered call is a strategy where you sell a call option on a stock you already own, earning a premium while capping potential profits. This is ideal when you own shares of a stock and believe its price will remain relatively stable or rise slightly.
Example:
You own 1,000 shares of Reliance Industries, purchased at ₹2,300 per share.
A short put involves selling a put option to collect premiums, expecting the stock price to stay above the strike price. Use this strategy if you believe the asset price will rise or remain stable.
Example:
Tata Motors is trading at ₹600.
However, if Tata Motors falls below ₹550, you may incur losses, as you’ll be obligated to buy the stock at ₹550, regardless of how much further it drops.
A married put involves buying a put option while holding the underlying stock. This strategy protects against downside risk while keeping the potential for upside gains. Use this strategy to protect your investment from sharp declines while benefiting from price increases.
Example:
You hold 1,000 shares of HDFC Bank, purchased at ₹1,700 each.
If the price rises above ₹1,700, you lose the premium but benefit from the stock's price appreciation.
They differ significantly regarding risk, obligations, and strategies. Options provide flexibility with limited risk, while futures carry higher risk but greater certainty for both buyers and sellers.
| Feature | Options Trading | Futures Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Obligation | No obligation to buy/sell; the buyer has the right. | Obligation to buy/sell the asset at contract terms. |
| Risk | Limited to the premium paid for buyers. | Higher risk; both buyers and sellers face unlimited loss potential. |
| Capital Requirement | Requires less upfront capital (premium only). | Requires higher margin as collateral. |
| Profit Potential | Gains depend on price movements before expiry. | Gains/losses depend directly on price at expiry. |
| Best Suited For | Speculation, hedging, and income generation. | Long-term hedging and speculative trades. |
Participants in options trading are categorized based on their roles in the market and their approach to the contracts. Here’s a breakdown of the key participants and their positions:
1. Option Buyers (Holders)
2. Option Sellers (Writers)
3. Call Option Participants
4. Put Option Participants
Familiarity with key terminologies is essential for navigating options trading. Here are the most important terms explained in simple words:
1. Premium
2. Expiry Date
3. Strike Price
4. American Option
5. European Option
6. Intrinsic Value
7. Index Options
The Greeks are key metrics that help options traders understand how different factors, like time and volatility, impact the price of an option. Below are the main Greeks explained briefly:
In options trading, profitability depends on whether the option is In-the-Money (ITM), Out-of-the-Money (OTM), or At-the-Money (ATM):
Options trading is an excellent choice for Indian investors exploring flexible and cost-effective trade methods. It allows you to profit from market movements, hedge risks, and generate income without owning the underlying asset outright. You can minimize risks and maximize gains with the right strategies and tools. However, success in options trading depends on a solid understanding of concepts like premiums, strike prices, and time sensitivity, making education and risk management key to achieving consistent results.
An option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset (like stocks) at a predetermined price before a specific date. Options are derivatives, meaning their value is linked to an underlying asset.
The best options trading strategies for beginners include long calls, long puts, and covered calls. These simple strategies limit risks while helping beginners understand market dynamics and options pricing.
The minimum capital required depends on the option's premium and its lot size. Since you only pay the premium upfront, trading options can start with relatively lower capital than buying stocks outright.
Options trading and stocks serve different purposes. Options are better for short-term gains, hedging, and leveraging small capital, while stocks are more suitable for long-term wealth creation. The choice depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
Options trading is primarily a skill that involves analyzing markets, understanding risk, and applying strategies. While market movements can sometimes be unpredictable, relying solely on luck is not a sustainable approach in options trading.
Popular tools for options trading in India include brokerage platforms like Lakshmishree and for better decision-making, traders can also use options trading indicators like RSI and Bollinger Bands. Check out our detailed article on the Best Options Trading Indicators to learn more.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes only. Please note that the data related to the mentioned companies may change over time. The securities referenced are provided as examples and should not be considered as recommendations.