
Liquidity in stock market measures how easily you can buy or sell stocks without affecting their price. This fundamental concept shapes the trading experience and influences the strategies of investors. Our article breaks down “what is liquidity in stock market”, why it’s crucial, and the factors that affect a stock’s liquidness —vital information for effective trading.
Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be converted into cash without significantly affecting its price. High liquidity indicates that an asset can be quickly sold or bought in the market at a price close to its true value. The concept is important in both personal finance and across various markets.
Examples of liquid assets include:
On the other hand, illiquid assets such as real estate or collectables are considered less liquid as they cannot be readily converted into cash without a potential loss in value.
In a broader sense, liquidity also encompasses the ability of individuals or companies to meet their short-term obligations or financial needs without incurring significant losses. This is where accounting liquidity comes into play, focusing on a company’s short-term financial health and ability to cover its current liabilities with its current assets.
In the stock market, liquidity refers to how easily shares of a company can be bought or sold without causing a significant change in the stock's price. High liquidity in stock market is crucial because it ensures smoother transactions for investors and traders, allowing them to enter or exit positions quickly.
Liquidity is a crucial factor to consider when trading or investing in the stock market, as it can affect the overall cost and efficiency of transactions.
Imagine you're selling 500 shares of Reliance Industries Limited (RELIANCE), one of India's largest and most actively traded companies. Here's how liquidity plays out:
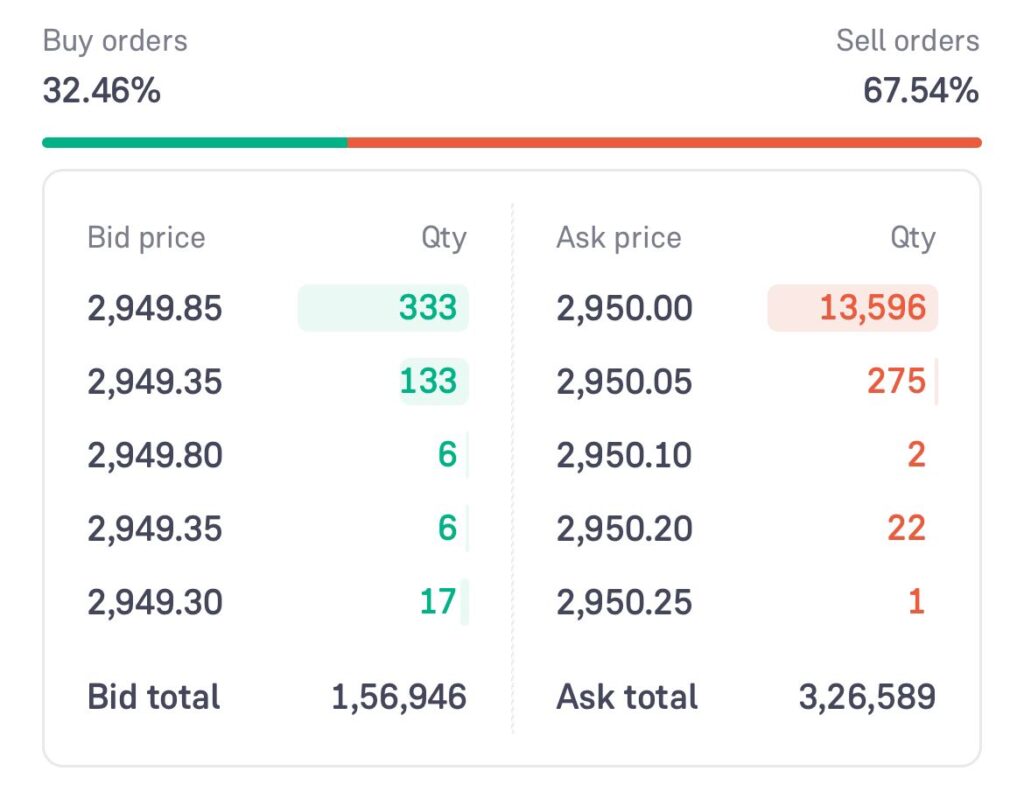
This example demonstrates how the liquidity in stock market, such as those of Reliance Industries, enables investors to trade efficiently and confidently, contributing to India's vibrant and dynamic stock market ecosystem.
However, not all securities are created equal in terms of liquidity. Some stocks, particularly those of large, well-known companies, are highly liquid and can be readily bought or sold. On the other hand, stocks of lesser-known or smaller companies may exhibit low liquidity, making them difficult to sell without impacting their price significantly. This highlights the importance of understanding liquidity risk, the risk that an investor might not be able to buy or sell securities when desired.
Certainly! In finance and stock market, there are 2 types of liquidity: market liquidity and accounting liquidity. Each type serves a different purpose and offers a unique perspective on managing assets and liabilities.
It refers to the extent to which a market, such as a stock market or real estate market, allows assets to be bought or sold at stable prices. High market liquidity means sufficient buyers and sellers anytime, enabling quick transactions without causing significant price changes. This is crucial for traders and investors who want to execute large transactions without impacting the market price too much.
Accounting liquidity is a financial metric used to determine how well a company can pay off its short-term debts using assets that can quickly be converted into cash. The term "accounting liquidity" comes into play because these measurements are derived from a company’s financial statements, specifically the balance sheet. This measure is crucial because it gives a snapshot of the company's financial health at any given time, focusing on its most liquid assets.
This is crucial for people who lend money to the company, like creditors and investors, because it shows whether the company is financially healthy and can handle its immediate financial obligations.
There are three main ways to measure how liquid, or cash-ready, a company is:


Market liquidity is composed of several key elements:

Liquidity is critical in the stock market for several reasons, affecting both the overall market environment and the individual strategies of investors. It plays a central role in the efficiency, stability, and accessibility of financial markets. Here are some key reasons why liquidity in stock market is highly valued:
High liquidity in the stock market means enough buyers and sellers are available to execute transactions quickly. This reduces the time and effort needed to buy or sell stocks, making the market more accessible for all participants, from small retail investors to large institutional traders.
Liquidity is essential in the stock market because it enhances the price discovery process, ensuring stock prices accurately reflect all available information. In highly liquid markets, frequent trading by a diverse range of participants helps quickly integrate new data into stock prices. This continual adjustment means prices represent what the market collectively values stocks based on the latest economic indicators and company-specific news.
Liquidity can act as a buffer against large price swings. In a highly liquid market, the impact of large trades on the stock's price is minimized because the volume of buy and sell orders can absorb larger transactions without significant price changes.
When investors know they can enter and exit positions at fair prices, they are more likely to invest in that market. This confidence boosts overall market participation and can attract both domestic and international investors, enhancing the capital formation necessary for economic growth.
Liquidity is crucial for institutional investors, who often deal with large quantities of stocks. It enables them to execute large orders without significantly affecting the stock's price, which can be crucial for maintaining portfolio performance and meeting strategic goals without disrupting the market.
Good liquidity in a stock is indicated by several essential factors that enhance the trading experience:
A stock with high trading volume has good liquidity, meaning many shares are traded daily, facilitating easy entry and exit for traders.
A narrow bid-ask spread suggests low transaction costs, as the price difference between buying and selling is minimal, indicating high liquidness.
Good liquidity is also seen in the market depth, where large orders can be absorbed without significantly affecting the stock's price, ensuring price stability.
It helps stabilize stock prices by absorbing large trades without major price shifts, which is important for investors managing significant assets.
In liquid markets, trades are executed quickly, allowing investors to take advantage of market conditions without delay.

Highly liquid markets facilitate smoother transactions for large volumes without significant price changes. Here are some of the most liquid financial markets globally and in India:
The Forex market is the largest and most liquid market in the world, with a vast amount of money being traded daily. Currencies need to be exchanged to conduct foreign trade and business, which keeps the Forex market highly liquid. For Indian traders, participating in the Forex market means they can easily buy and sell currencies without worrying about large price impacts.
Globally, major stock exchanges like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and the NASDAQ are known for their high liquidity. In India, the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE) are highly liquid trading venues. These exchanges facilitate the trading of stocks of numerous companies, including major Indian conglomerates and multinationals, allowing investors to enter and exit positions with relative ease.
The market for government securities, such as Treasury bonds in the United States and government bonds in India (issued by the Central and State governments), is highly liquid. These bonds are backed by the government, making them low-risk, which in turn attracts a large number of investors—both retail and institutional. This makes it easier to buy and sell these securities in the market.
Various factors cause liquidity in stocks to vary. For instance, stocks with high trading volumes usually attract more interest from various market participants, enhancing their liquidity. Moreover, market makers, who ensure a stable market with tight bid-ask spreads, contribute to the liquidity of stocks.
On the contrary, illiquid stocks often have wider bid-ask spreads and less market depth, usually because of lower trading volume and notoriety. For example, a large multinational company's stock is typically more liquid than that of a smaller regional company.

Several factors can indicate a stock’s liquidity level, including:
High trading volumes suggest that a stock is in demand. On the other hand, a narrow bid-ask spread typically indicates a liquid stock, whereas a wide bid-ask spread signals that a stock may be illiquid.

Understanding liquidity in the Indian stock market can be clarified by examining real-world examples illustrating how liquidity in stock market impacts trading and investment. Here are a few scenarios showcasing liquidness in action within the context of major Indian financial instruments and markets:
Reliance Industries, a major player in India’s stock market, showcases high liquidity with its significant daily trading volume on the NSE and BSE. This ensures minimal price shifts and lower transaction costs due to narrow bid-ask spreads when trading its shares.
The Zomato IPO in 2021 experienced high demand and significant trading volume on its debut, allowing for the stable trading of many shares without drastic price changes. Such liquidity is essential during IPOs to ensure price stability and accurate stock valuation.
The Nifty Bank ETF, tracking the NSE banking sector index, is highly liquid, similar to trading individual stocks. It benefits from the liquidity of underlying major bank stocks, facilitating easy buying and selling, which is crucial for diversified investment strategies.
India’s 10-year government bonds are highly liquid, enabling large transactions without notable price fluctuations. This reflects strong market confidence and steady demand from institutions like banks and insurance companies.
The 2016 demonetization in India starkly impacted cash liquidity, as the withdrawal of high-value notes made it challenging for the public to access new or smaller denominations. This event underscored the importance of cash liquidity in maintaining economic stability and supporting daily transactions.
In a nutshell, liquidity is a vital aspect of financial markets that impacts everything from the execution of trades to the stability of asset prices. Understanding what is liquidity in stock market is particularly crucial as it directly influences how easily stocks can be bought or sold without significantly affecting their price. Whether it’s assessing the liquidity of a particular stock in the stock market or managing the liquidness of personal financial assets, grasping this concept is essential for investors and individuals alike.
Liquidity is the ease with which an asset or security can be bought or sold without impacting its market price, and it also pertains to the ability of individuals or companies to meet short-term financial obligations without incurring substantial costs.
The difference between accounting liquidity and market liquidity is that accounting liquidity pertains to an entity's ability to meet financial obligations using liquid assets, whereas market liquidity relates to the ease of buying or selling stocks without affecting their prices significantly.
You can measure a stock's liquidity level by examining its trading volume, bid-ask spread, market depth, and order book data. Understanding these factors can provide insight into the stock's ease of trading and price stability.
Yes, high liquidity is generally considered good because it allows for easier and quicker buying and selling of assets without significantly impacting their prices. This results in better price stability, lower transaction costs, and greater overall efficiency in the market.
It is calculated by evaluating key metrics such as trading volume, where higher volumes suggest greater liquidity; bid-ask spread, with narrower spreads indicating higher liquidity; and market depth, which assesses the volume of buy and sell orders at various price levels near the market price, with greater depth pointing to increased liquidness.
High liquidity is generally better in the stock market as it facilitates easier transactions, allowing stocks to be bought or sold quickly without significantly affecting the price. It also lowers transaction costs due to narrower bid-ask spreads, contributes to price stability by absorbing large orders without drastic price changes, and enhances price discovery, ensuring stock prices accurately reflect the most current market information.
