
Choosing the right trading strategy can be a tough decision for many traders. Should you go for quick trades with fast profits, or is it better to hold on for a bit longer to catch bigger market moves? This is where the debate between scalping vs swing trading comes into play. Both strategies offer different paths to success, but which one is the right fit for you?
This blog breaks down the key differences between scalping and swing trading, helping you find the approach that matches your goals and style. Keep reading to discover which trading method could work best for you!
When it comes to trading in the stock market, scalping and swing trading are two popular strategies. Scalping is all about quick trades to grab small profits, often even within minutes. Swing trading will look more toward catching larger movements in price over a few days or even weeks. Both methods have their set of advantages and challenges. While scalping demands a lot of attention and quick decision-making, swing trading gives more time to analyze the markets.
Scalping is a rapid method of stock trading in which the stock traders, known as scalpers, attempt to make a profit based on small price fluctuations. In contrast to other market players who trade within a large timeframe, the scalper will open and close a position in the market within a short time, mostly seconds or just a few minutes within the market. Therefore, the basic idea of scalping is to catch small price moves in the market, widening its share to increase the potential profit.
Scalping focuses on smaller market movements, relying on technical analysis while having a short time horizon. They usually close all their positions before the market session ends, making scalping an intraday trading strategy.
However, scalping should not be confused with regular intraday trading. While both are conducted intra-day, the time frames on scalping are much shorter and include numerous more trades to gain small price changes, while intraday trading involves a few trades within the day and slightly longer holding periods. This requires speedy responses that support high concentration levels.
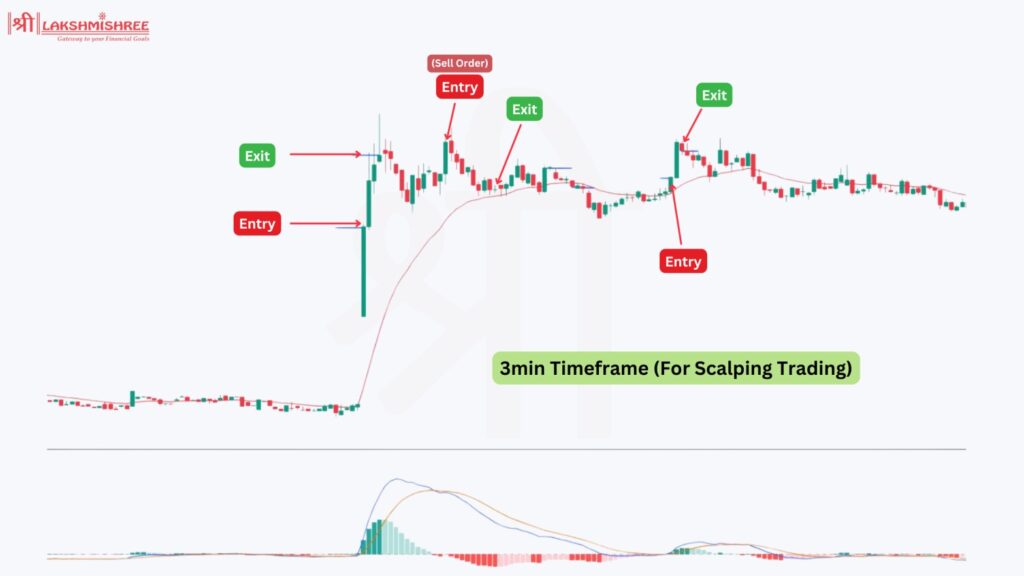
Scalping can be an effective strategy for those who thrive in fast-moving environments and are comfortable making quick decisions. However, a disciplined approach and a strong understanding of technical analysis are required to succeed.
Swing trading involves traders seeking to gain profits by simply holding trades for a few days or even weeks. It differs from scalping or even day trading, where one sells the trade instantly or within a short time. In swing trading, more time is given to the development of a trade into its target. In this form of trading style, traders seek medium-term trading opportunities and wait for price "swings" to make a profit.
Swing traders will generally combine fundamental and technical analysis to search for possible market setups. They will usually look at various swing trading patterns and use swing trading indicators, such as moving averages, RSI, or Fibonacci retracements, to help predict the market's moves.
The best time frame for swing trading often includes daily or 4-hour charts, allowing traders to spot trends and key levels of support and resistance clearly.
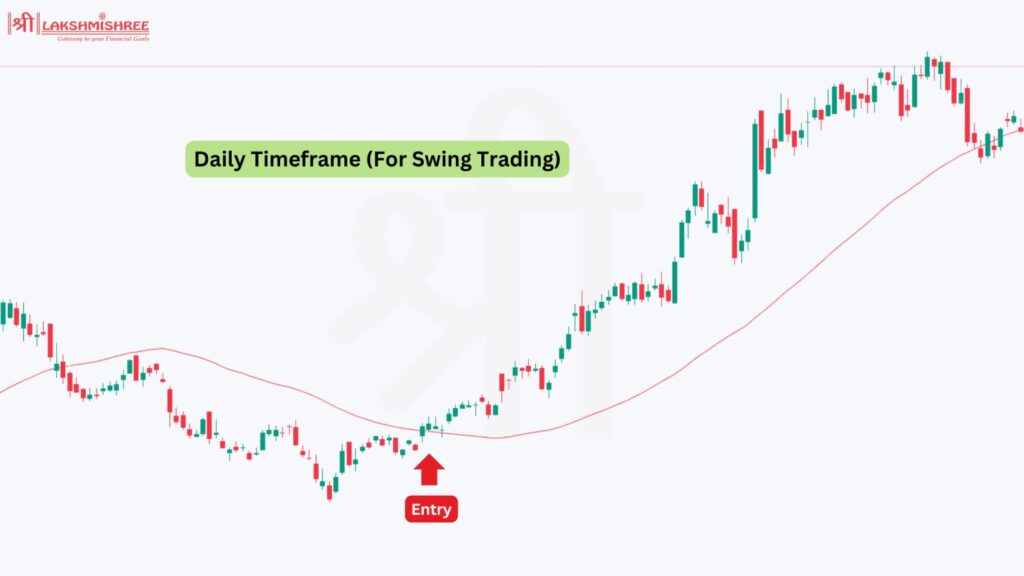
Swing trading is less intense than scalping; therefore, it is suitable for those who do not like to sit in front of the screen watching the markets but are active traders.
Swing trading could be ideal for anyone seeking a balanced approach between fast-paced day trading and long-term investing, but it comes with its own set of challenges. It’s important to carefully weigh these pros and cons to see if this strategy aligns with your trading style and financial goals.
To help you better understand the differences between scalping vs swing trading, here’s a quick comparison table highlighting the key aspects of each strategy:
| Factor | Scalping | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Holding Period | Seconds to minutes; rarely a few hours | Several days to weeks |
| Frequency of Trades | Very high; multiple trades per day | Lower; a few trades per week |
| Chart Timeframe | 1-minute to 5-minute charts | 4-hour to daily charts |
| Persona | Quick thinkers who thrive under pressure | Patient traders who prefer taking time to analyze trends |
| Risk Tolerance | High; trades must be closely monitored | Moderate; more time to react to market movements |
| Leverage Usage | High leverage to amplify small price changes | Typically lower leverage, focusing on larger price movements |
| Market Analysis | Primarily technical analysis with a focus on quick setups | Combination of technical and fundamental analysis |
| Stress Level | High stress due to rapid decision-making | Moderate stress with more time to plan trades |
Scalping and swing trading come with their own risks, but many traders consider scalping riskier due to its fast-paced nature. In scalping, a trader has to think very fast because he has only seconds to decide. Besides that, the frequency is higher in scalping; therefore, it enhances transaction costs and may result in huge losses if the market suddenly goes against your position.
Swing trading is also a bit risky; however, the time given to study the market and make decisions is more and, therefore, less potential to act on impulse. At the same time, swing traders also have overnight risks and potential gaps that may morph into losses.
Deciding between scalping vs swing trading depends on your personality, time availability, and risk tolerance. If you thrive on adrenaline, enjoy making quick decisions, and have time to monitor the markets closely, scalping might be the right fit for you. It requires a sharp focus and the ability to handle stress. On the other hand, swing trading could be better if you prefer a more relaxed approach with time to analyse and plan.
Swing trading allows for a more balanced lifestyle, making it suitable for those who can’t watch the markets all day but still want to trade actively. Consider your goals, how much time you can dedicate to trading, and how you handle risk when choosing your strategy.
For both scalping and swing trading, having the right tools and resources is crucial for success. Here are some key tools and indicators used by traders:
Having these tools at your disposal can help you navigate the complexities of the market, whether you’re scalping for quick profits or swing trading for larger moves.
Choosing between scalping vs swing trading ultimately depends on your personal trading style, risk tolerance, and available time. Scalping is ideal for those who thrive on quick decisions and can manage high stress, while swing trading suits those who prefer a slower pace with more analysis. Whatever you choose, understanding each strategy’s strengths and weaknesses will help you make informed decisions and increase your chances of success in trading.
Scalping involves making quick trades to capture small price movements, while swing trading focuses on capturing larger price swings over a few days or weeks.
Swing trading is generally considered better for beginners because it allows more time for decision-making and requires less screen time.
Yes, scalping relies heavily on short-term indicators and real-time data, while swing trading focuses on tools that help identify trends and larger market movements over longer periods.
Profitability depends on the trader’s skill, market conditions, and strategy execution. Scalping can provide quick, smaller profits, while swing trading aims for larger gains over time. Both have potential for profits but require different approaches and risk management.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your research and consider consulting with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.