
Ever wondered how some traders make money by simply holding onto their investments for months or even years? You might be curious about a different approach if you’re tired of the stress and quick decisions involved in day trading. But what is positional trading, exactly? This strategy focuses on long-term gains by identifying and holding onto promising investments through market ups and downs.
In this blog, we’ll break down positional trading meaning and how you can use it to your advantage, without the headache of constant market monitoring.
Positional trading is a long-term investment strategy where traders hold onto their assets for an extended period—typically weeks, months, or even years—to capitalize on major market trends. Unlike other trading styles, which focus on short-term gains and require constant monitoring, positional trading takes a more patient approach, allowing the market to move in favour of the trader’s prediction over a longer timeframe.
This strategy relies heavily on identifying the market's overall direction, using a mix of fundamental and technical analysis. Fundamental analysis involves assessing the underlying value of an asset, such as a company's financial health, market conditions, or economic indicators. On the other hand, technical analysis examines historical price movements and patterns to predict future trends. By combining these methods, positional traders aim to enter a trade at an optimal time and hold it until the market conditions align with their expectations.
However, positional trading isn't just about picking a stock and waiting. It requires careful planning, risk management, and the ability to withstand market volatility without making impulsive decisions. The key is to stay focused on the long-term trend rather than getting distracted by short-term market noise.
Positional trading involves holding assets for a longer period to capitalise on major market trends rather than short-term price movements. This strategy requires a solid understanding of market dynamics and careful planning. The main idea is to identify a trend early and hold the position until the trend reaches its peak or reverses. The process typically involves three key steps: identifying a trend, entering a position, and holding it over time with a clear exit strategy in mind.
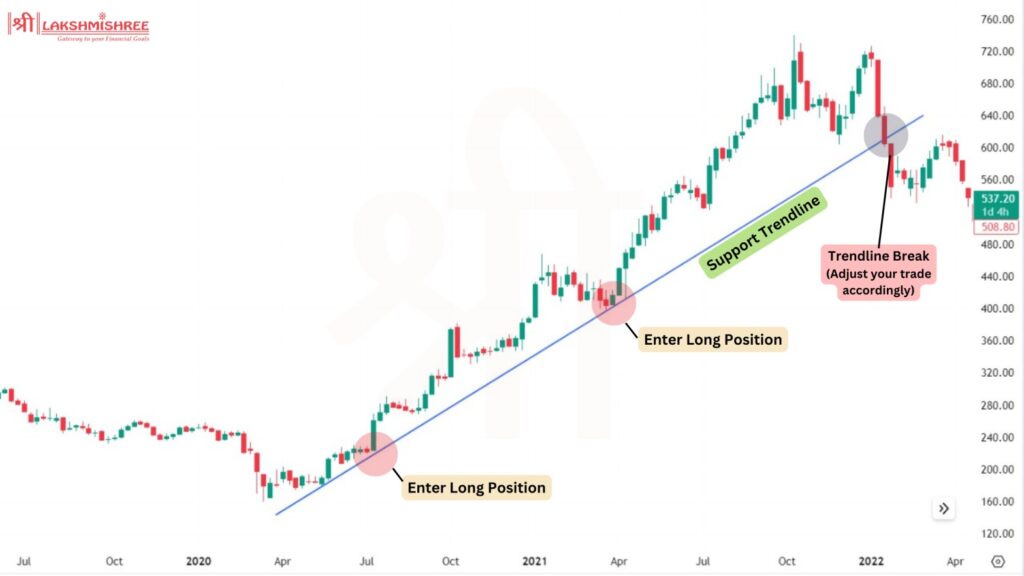
Identifying a trend is crucial in positional trading, as it helps traders decide when to enter or exit a market. Trends are identified using a mix of fundamental analysis, technical analysis, and macroeconomic factors:
While positional trading can offer significant rewards, it has several challenges and risks that traders must consider carefully. One major downside is the exposure to market risks over an extended period. Holding positions for weeks, months, or even years makes traders vulnerable to unexpected events like economic downturns, political instability, or sudden market changes, which can lead to substantial losses if the market moves against them.
Another key risk is the opportunity cost associated with long-term positions. By focusing on long-term trends, traders might miss out on short-term opportunities and quick gains that could arise in the market. This lack of flexibility can be a disadvantage, especially in rapidly changing market conditions.
Additionally, positional trading requires a high level of patience and discipline. Traders must avoid reacting impulsively to short-term market fluctuations and stay committed to their long-term strategy. This can be challenging during periods of market volatility or when positions go against expectations.
Lastly, high capital requirements can be a barrier for some traders. Maintaining positions over a long period often requires substantial capital to withstand potential drawdowns and avoid prematurely exiting a position. Without sufficient funds, traders may find it difficult to stay invested through market ups and downs, increasing the risk of significant losses.
While many traders are interested in positional trading, the challenge often lies in finding the right tools and support to execute these strategies effectively. At Lakshmishree, we offer comprehensive trading solutions and research support, making it easier for you to navigate the market and seize long-term opportunities confidently.
Traders use several strategies to make the most of positional trading. These strategies are designed to help traders maximise profits while managing risks:
Positional trading comes with several advantages that make it appealing to many investors:
To make informed decisions, positional traders rely on various indicators and tools that help identify trends and determine the best entry and exit points:
Both position trading and swing trading are popular strategies, but they cater to different types of traders based on their time commitment and risk tolerance. While position trading focuses on long-term trends, often holding assets for several months or even years, swing trading aims to capture short to medium-term gains by holding assets for a few days to a few weeks. Here's a quick comparison to highlight the key differences:
| Aspect | Position Trading | Swing Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Time Frame | Weeks to years | A few days to a few weeks |
| Market Focus | Long-term trends | Short to medium-term price movements |
| Trading Frequency | Low – few trades per month or year | Moderate – several trades per month |
| Risk Level | Potentially higher due to long exposure, but generally lower due to fewer trades | Moderate, with the need for quick decision-making in volatile conditions |
| Capital Requirement | Higher, as traders need to withstand longer drawdowns and maintain positions | Lower, as trades are shorter, allowing for more frequent opportunities |
| Stress Level | Lower – less monitoring required, suited for those with a long-term outlook | Higher – requires more active management and monitoring |
| Focus on Analysis | Fundamental analysis combined with technical indicators | Primarily technical analysis to catch price swings in the short term |
So, what is positional trading? At its core, positional trading is about capturing long-term market trends to maximize potential profits. Unlike short-term strategies that focus on quick gains, positional trading requires patience, discipline, and a solid understanding of market fundamentals and technical indicators. By holding positions over an extended period, traders aim to ride out market volatility and capitalize on significant price movements.
However, this strategy also comes with risks, such as exposure to prolonged market downturns and the need for substantial capital.
Passive investors generally buy and hold assets for a long time without active management, focusing on portfolio growth over decades. Position traders, however, actively manage their long-term positions to capitalize on market trends.
An open position in trading is a trade that has been entered into but not yet closed, meaning the trader still holds the asset and is exposed to market movements.
The best time frame for positional trading typically ranges from days to weeks. It depends on the asset being traded and the market conditions.
A long position involves buying an asset expecting its price to increase, while a short position involves selling an asset with the intention of buying it back later at a lower price.
The amount of capital needed varies depending on the asset and market. However, a larger capital base is often required to withstand potential drawdowns over long periods.
Yes, positional trading can be automated using trading algorithms and software that follow specific rules to manage entries and exits based on pre-defined strategies.
Common mistakes include over-leveraging, lack of patience, ignoring market fundamentals, and failing to set stop-loss orders to manage risk effectively.
Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your research and consider consulting with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.