
If you’ve ever considered investing in the stock market, you’ve probably heard terms like “equity shares” and “preference shares” tossed around. But what's the difference between equity and preference shares, and why does it matter? These shares aren’t just financial jargon—they’re two distinct ways to own a piece of a company, each with its own perks and pitfalls.
In this guide, we’ll break down the difference between equity and preference shares so you can make smarter investment choices. Whether you’re looking for higher returns or a more stable income, understanding these options can help you find the right fit for your financial goals.
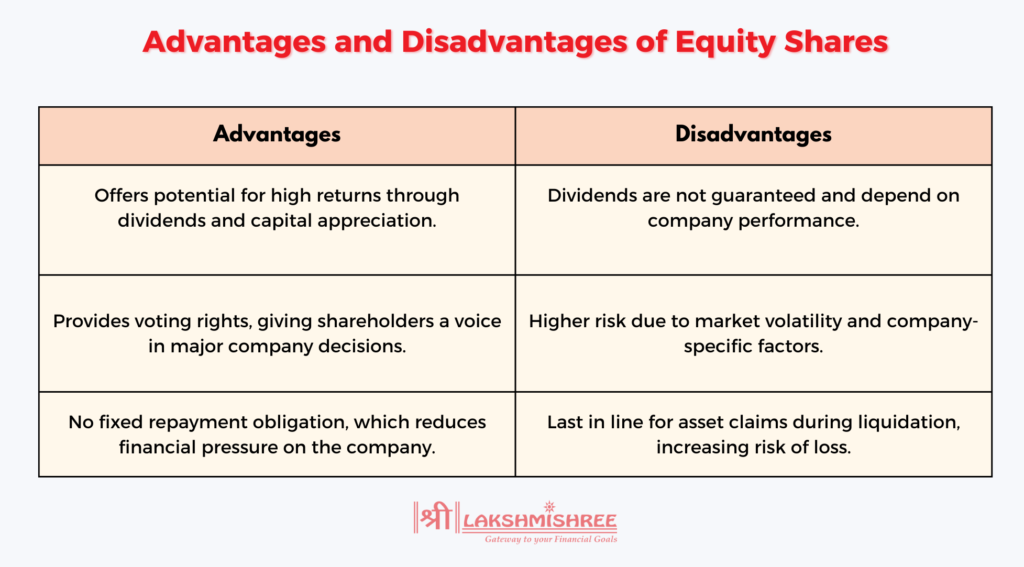
Equity shares, also known as ordinary shares, signify partial ownership in a company. When you hold equity shares, you are entitled to a portion of the company's profits, which are distributed as dividends, though these are not guaranteed and fluctuate with the company’s performance. Equity shareholders are often regarded as the true owners of the company since they bear both the risks and rewards of the business.
One key aspect of equity shares is giving shareholders voting rights, allowing them to influence critical decisions, such as electing board members or approving major company policies. Additionally, equity shareholders stand to benefit from capital appreciation if the company’s stock value increases over time, providing potential for significant long-term gains. However, in the event of liquidation, equity shareholders are last in line to receive any remaining assets after all debts and other liabilities are settled.
DVR shares, or Differential Voting Rights shares, are a unique type of equity share that provides varied voting rights compared to ordinary equity shares. In most cases, DVR shares offer fewer voting rights per share but compensate investors with higher dividends. These shares appeal to investors more interested in income than control, as they offer enhanced returns without the burden of frequent decision-making power.
However, DVR shares are relatively rare in the Indian stock market, with only a handful of companies currently offering them. DVR shares can be a good choice for investors seeking higher income but with less interest in voting on company matters.
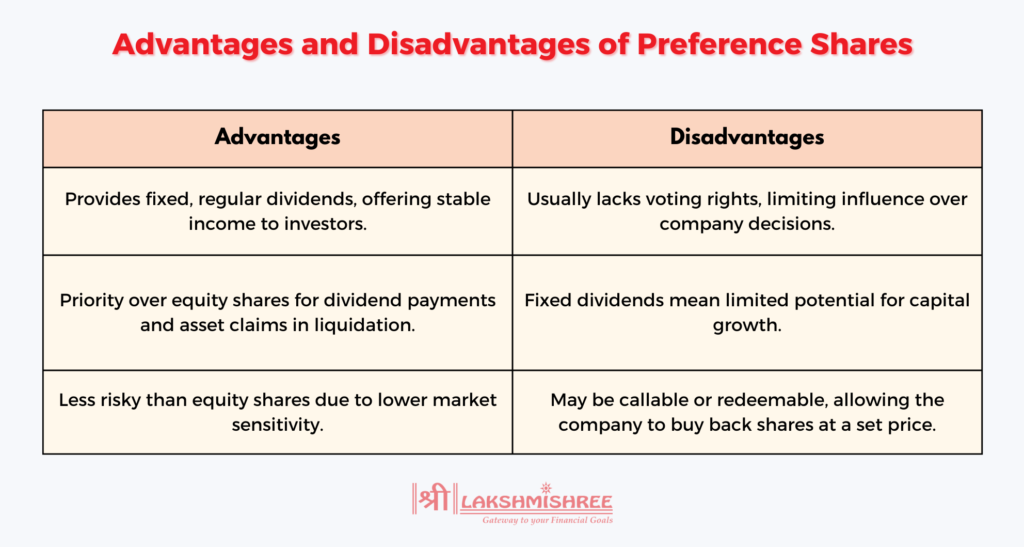
Preference shares, sometimes referred to as preferred stock, represent a different class of ownership in a company. Unlike equity shares, preference shares come with a fixed dividend that is paid out before any dividends to equity shareholders, providing a more predictable income stream. Preference shareholders have priority over equity shareholders in the payment of dividends and also in the event of liquidation, where they are repaid before equity holders, though after all debts are cleared.
However, preference shares generally do not have voting rights, meaning preference shareholders typically have little say in the company's day-to-day management or strategic decisions.
Equity shares represent ownership in a company and provide voting rights, allowing shareholders to influence company decisions. However, they carry higher risks, as dividends fluctuate with profits. Preference shares, on the other hand, offer fixed dividends and give priority over equity shares when it comes to payouts and claims on assets. Though they usually lack voting rights, preference shares are favoured by investors seeking steady income and lower risk.
Now, let’s break down the specific differences between equity shares and preference shares in more detail:
| Parameter | Equity Shares | Preference Shares |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ownership share with voting rights | Share with preferential dividend and asset claim rights |
| Dividend Payout | Variable, depends on company profits | Fixed, regular payout regardless of profit levels |
| Dividend Rate | Fluctuates according to earnings | Fixed rate, often predetermined |
| Voting Rights | Yes, shareholders can vote in company matters | Typically no voting rights |
| Priority in Payout | Paid after preference shares in liquidation | Paid before equity shares |
| Growth Potential | High potential, tied to company performance | Limited to fixed dividends |
| Risk Level | Higher due to market volatility | Lower, with guaranteed dividend payouts |
| Bonus Shares | Eligible to receive bonus shares | Generally not eligible for bonus shares |
| Convertibility | Non-convertible | Can be either convertible or non-convertible |
| Redemption | Non-redeemable, held indefinitely | Can be redeemable or non-redeemable |
| Capital Repayment | Last in line during company liquidation | Repaid before equity shares |
| Arrears of Dividend | No entitlement to unpaid dividends | Cumulative shares may receive unpaid dividends in future years |
When comparing equity shares, preference shares, and debentures, it’s essential to understand how each serves a unique purpose in financing and investment. Debentures are a form of debt rather than equity, meaning they don’t represent ownership in a company. Instead, debenture holders are creditors who lend money to a company in exchange for a fixed interest rate over a set period. Unlike equity and preference shares, debentures don’t provide dividends or voting rights but offer lower risk and priority in repayment.
| Parameter | Equity Shares | Preference Shares | Debentures |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nature | Represents ownership | Represents partial ownership with fixed dividends | Represents debt; company borrows funds from investors |
| Return | Dividends and capital appreciation | Fixed dividends | Fixed interest payments |
| Voting Rights | Yes | Typically no | No |
| Risk Level | Higher, due to market volatility | Lower than equity, higher than debentures | Lowest risk among the three |
| Repayment Priority | Last in liquidation | Before equity shares | Priority over both equity and preference shares |
| Investment Type | Growth-oriented | Income-oriented | Income-oriented, low risk |
| Security | Unsecured | Unsecured, unless specified otherwise | Can be secured or unsecured, often backed by assets |
Debentures offer an alternative to equity and preference shares, allowing investors to choose based on their financial goals and risk tolerance.
Choosing between equity shares and preference shares depends on your investment strategy, risk tolerance, and income needs. Equity shares are ideal for those who want to participate in a company’s growth and decision-making actively. They offer higher potential returns through capital gains and dividends but come with greater risks, as they’re affected by market fluctuations.
Preference shares, however, are better suited for investors prioritising steady income over growth. With fixed dividends and priority over equity shares in asset claims, preference shares are less volatile, making them appealing to risk-averse investors.
When choosing between equity shares and preference shares, consider how each aligns with your financial goals:
In summary, equity shares are ideal for investors who want growth and are willing to accept more risk, while preference shares are better for those who seek steady income and prefer lower risk.
The difference between equity and preference shares comes from risk, return, and control. Equity shares provide ownership rights and the potential for high returns, but they carry more risk and are influenced by market changes. Preference shares, on the other hand, offer fixed dividends and priority in asset claims, making them more stable but with limited growth potential. Both types of shares have their own unique advantages, and choosing the right one depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance.
The main difference between equity and preference shares is that equity shares represent ownership with voting rights and potential for high returns, while preference shares provide fixed dividends, priority in dividends and asset claims but usually lack voting rights.
Yes, preference shares are generally considered safer because they offer fixed dividends and priority in payouts over equity shares, making them less volatile.
In some cases, yes. Certain types of preference shares are convertible, meaning they can be converted into equity shares after a specified period or under certain conditions.
No, equity dividends depend on the company's profits and are not guaranteed. Dividends may vary or even be skipped if the company doesn’t perform well.
Preference shareholders are paid before equity shareholders in the event of liquidation. However, debenture holders and other creditors are paid even before preference shareholders.
It depends on your goals. Equity shares offer long-term growth potential, while preference shares provide stable income. For growth, equity is better; for stable returns, preference shares are preferable.
Disclaimer: This article is intended for educational purposes only. Please note that the data related to the mentioned companies may change over time. The securities referenced are provided as examples and should not be considered as recommendations.